ACLS Algorithms - Updated 2020 AHA Guidelines
American Heart Association (AHA) updates the guidelines of CPR/ECC courses every 5 years. Below we review the 2020 updates. More can be found in 2020 AHA Guidelines.
The Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) algorithm is a systematic, evidence-based approach designed by the American Heart Association to guide healthcare providers in the urgent treatment of patients suffering from cardiac arrest, arrhythmias, stroke, and other life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies that compromise circulation or breathing. The American Heart Association revises the ACLS algorithm every five years to integrate the latest scientific evidence and medical innovations into treatment guidelines.
Rooted in the latest clinical research by the American Heart Association (AHA), the ACLS algorithm outlines precise sequences of actions and interventions. The algorithm aims to stabilize the patient in life-threatening conditions and maximize the chances of survival and good neurological outcomes. Familiarity with the algorithms is vital for clinicians in emergency, intensive care units, and certain primary care settings as it serves as a roadmap to ensure swift, organized, and effective care in high-pressure situations where every second counts.
Following are the core ACLS algorithms important to remember and simplify the step-by-step treatment process of a patient. These algorithms are important to understand and memorize in order to pass your ACLS exam. Your mastery of these ACLS protocols will undoubtedly save many lives.
- ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
- ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm
- ACLS Tachycardia Algorithm
- ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
- ACLS Suspected Stroke Algorithm
- ACLS Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm
- Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy Algorithm
- Opioid-Associated Life-Threatening Emergency Algorithm.
Algorithms for Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support You Need To Know
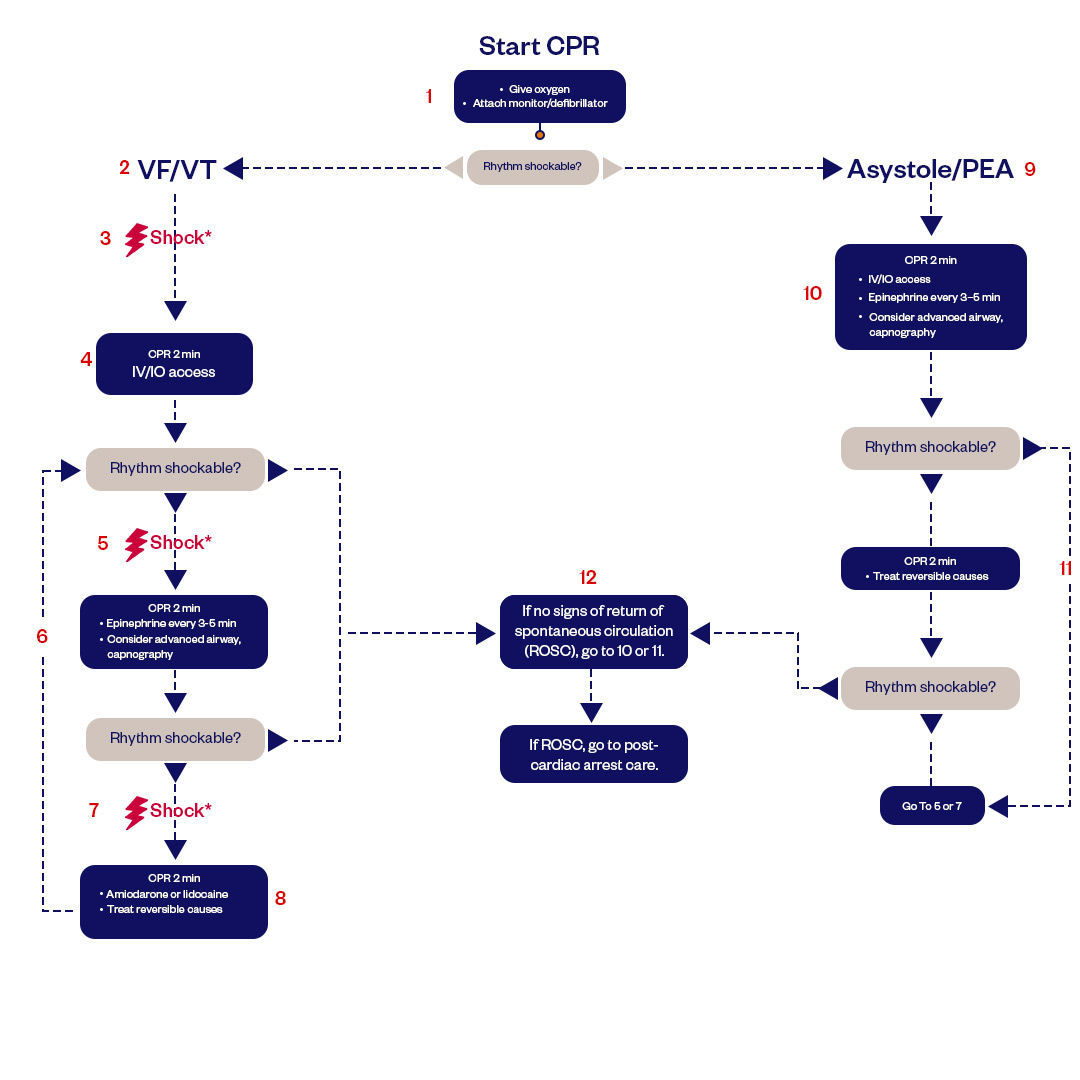
ACLS Algorithm #1: Cardiac Arrest
The adult cardiac arrest algorithm guides emergency treatment for sudden cardiac arrest. It's part of the Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) guidelines. This algorithm stresses quality CPR, quick defibrillation, and advanced care. First, confirm cardiac arrest. Then, start CPR and defibrillate if there's a shockable rhythm. The ACLS secondary assessment checks for shockable or non-shockable rhythms. Depending on the rhythm, give the right medications. Also, look for reversible causes, remembered as "H's and T's." Finish with post-arrest care. This approach aims to improve adult cardiac arrest and patient outcomes.
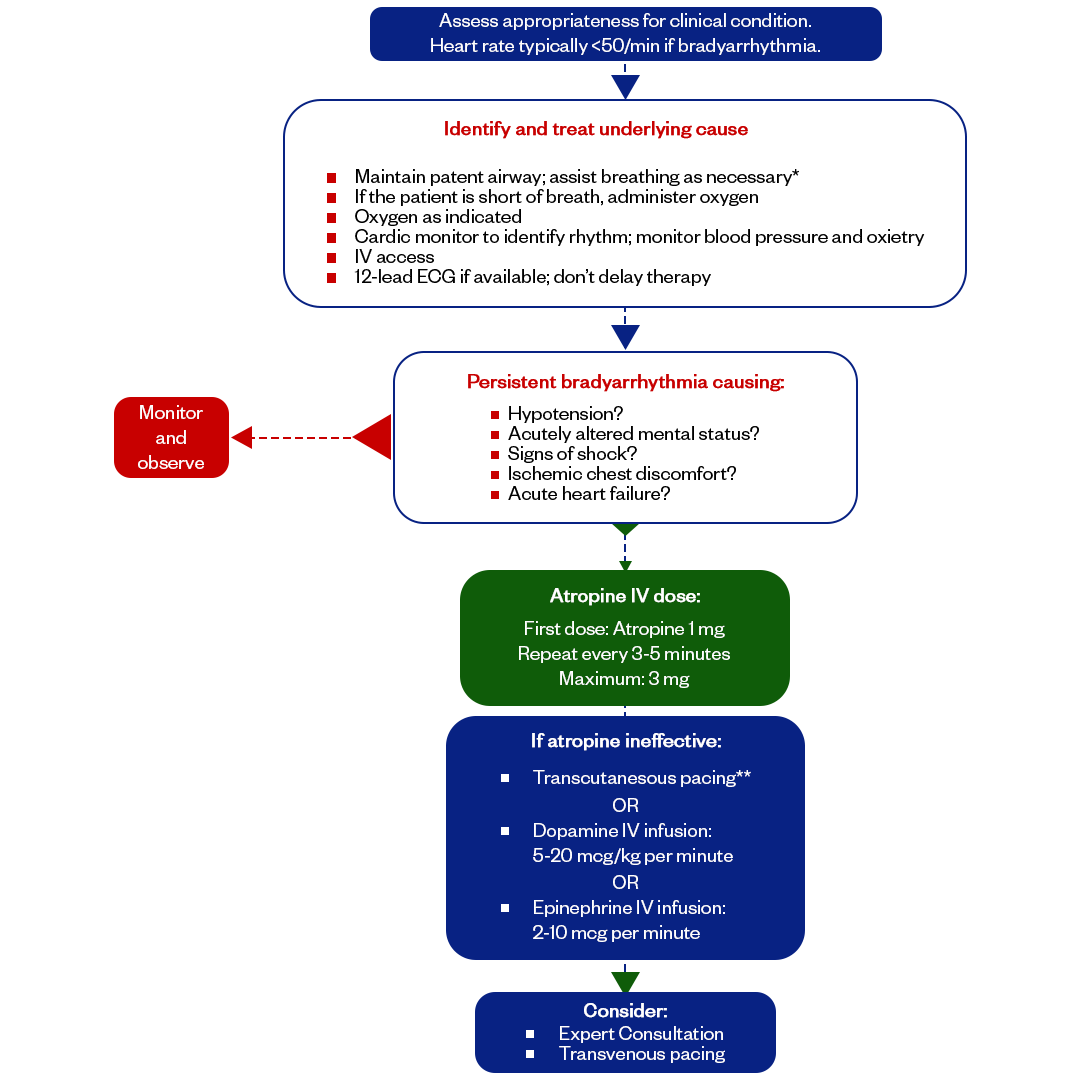
ACLS Algorithm #2: Bradycardia
The Bradycardia Algorithm in Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) guides the management of adults with symptomatic bradycardia. Initially, healthcare providers should recognize the condition, typified by a heart rate under 60 bpm with symptoms like hypotension or altered mental status. Immediate interventions include 2nd° heart block type II and 3rd° heart block type. The algorithm's primary goal is to quickly address life-threatening symptoms linked to bradycardia.
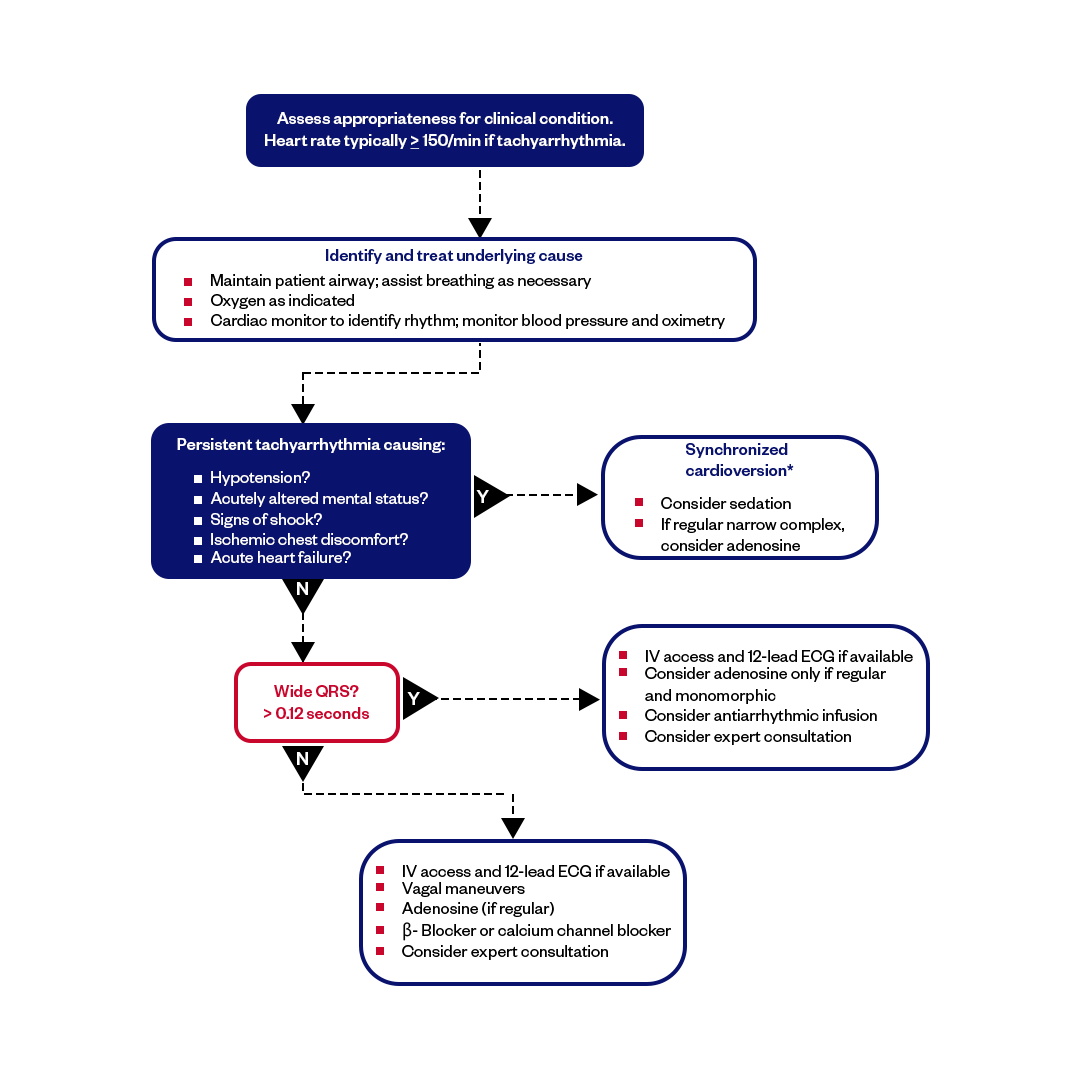
ACLS Algorithm #3: Tachycardia
The Tachycardia algorithms in ACLS guide treatment for rapid heart rhythms. Tachycardias are categorized as ventricular or supraventricular. For unstable tachycardia with symptoms like hypotension or altered mental status, immediate synchronized cardioversion is recommended. If pulseless, follow the VT or VF ACLS algorithms. For stable tachycardia, narrow complexes may indicate Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT). Wide complexes suggest potential VT, with treatments like amiodarone considered. Addressing underlying causes (e.g., electrolyte imbalances) is vital. The Tachycardia algorithm's aim is to quickly manage life-threatening arrhythmias.
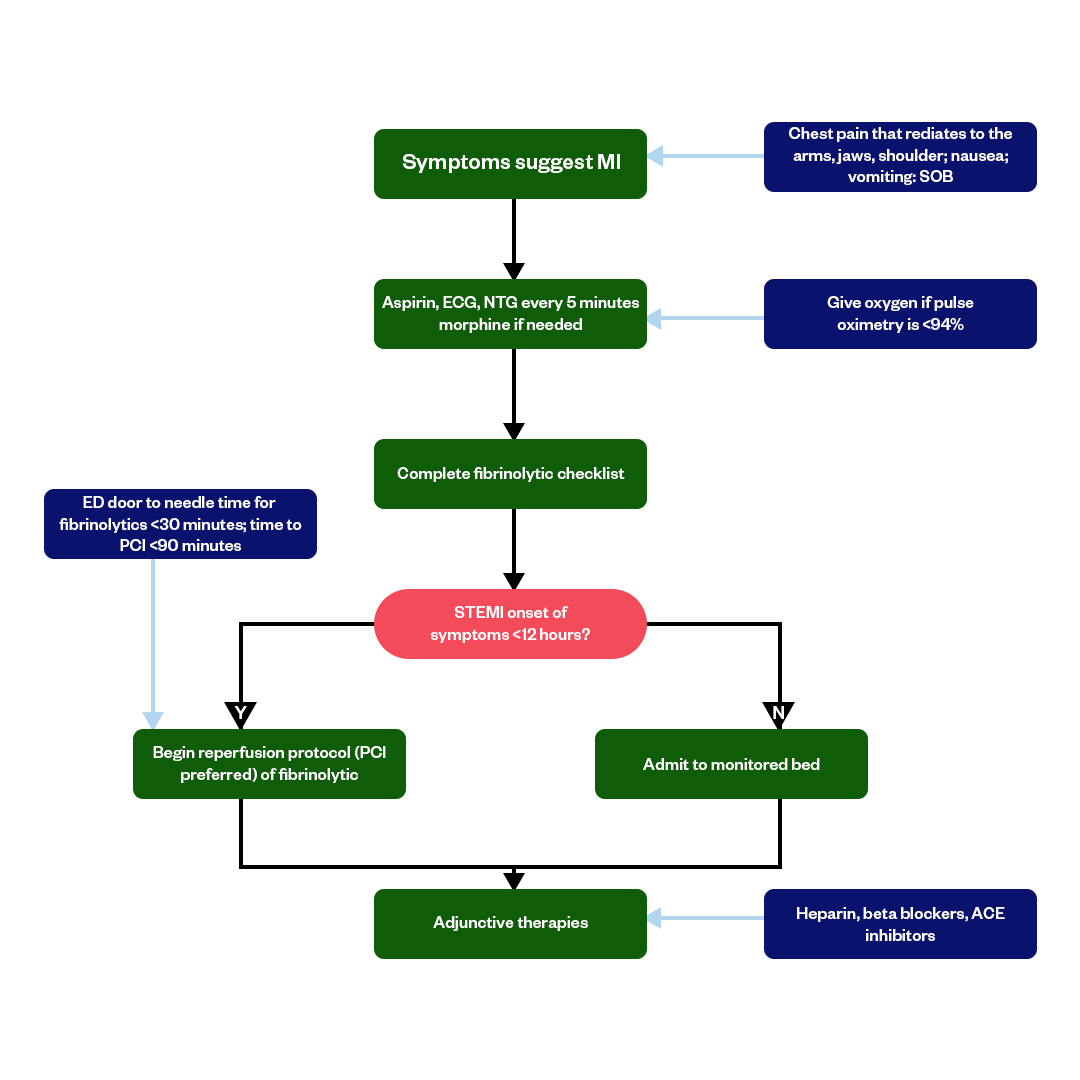
ACLS Algorithm #4: Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) algorithm in ACLS directs care for patients with acute coronary syndrome. Initially, it focuses on recognizing and assessing chest pain or discomfort and other ACS symptoms. Immediate steps include ensuring a patent airway, administering oxygen if needed, continuous ECG monitoring, and obtaining a 12-lead ECG to diagnose ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) or non-STEMI. Based on the ECG findings, the pathway splits: patients with STEMI might proceed to immediate reperfusion therapy, typically percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). While non-STEMI patients are managed based on risk stratification. The Acute Coronary Syndrome algorithm’s primary aim is the identification and treatment of STEMI.
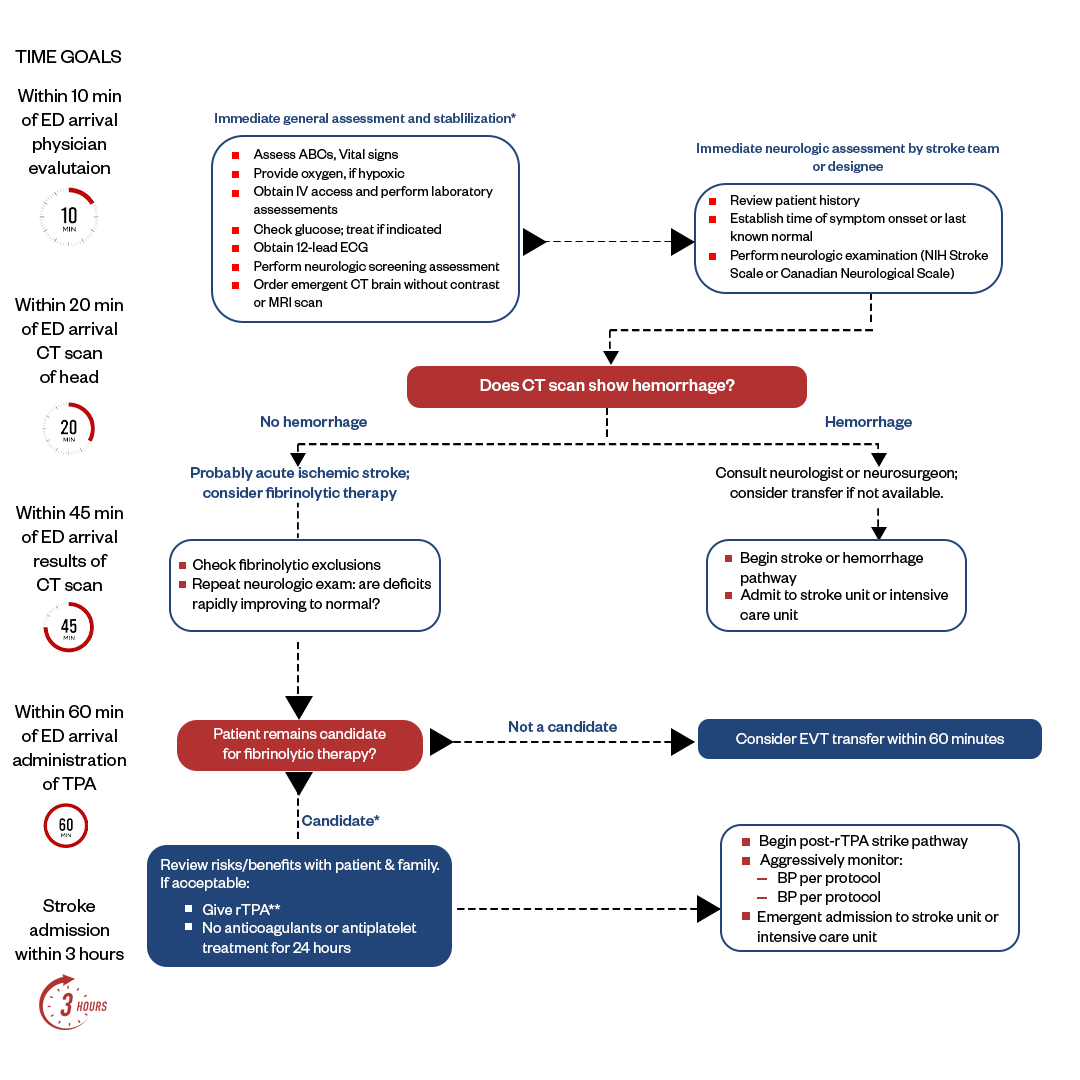
ACLS Algorithm #5: Suspected Stroke Algorithm
The Suspected Stroke Algorithm aims to quickly identify and manage potential stroke patients. It prioritizes timely assessment using tools like the FAST (Face, Arms, Speech, Time) exam. Crucially, a non-contrast CT scan is obtained to differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. This distinction guides treatment, with ischemic stroke candidates evaluated for clot-busting medications. Time is of the essence, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce disability.
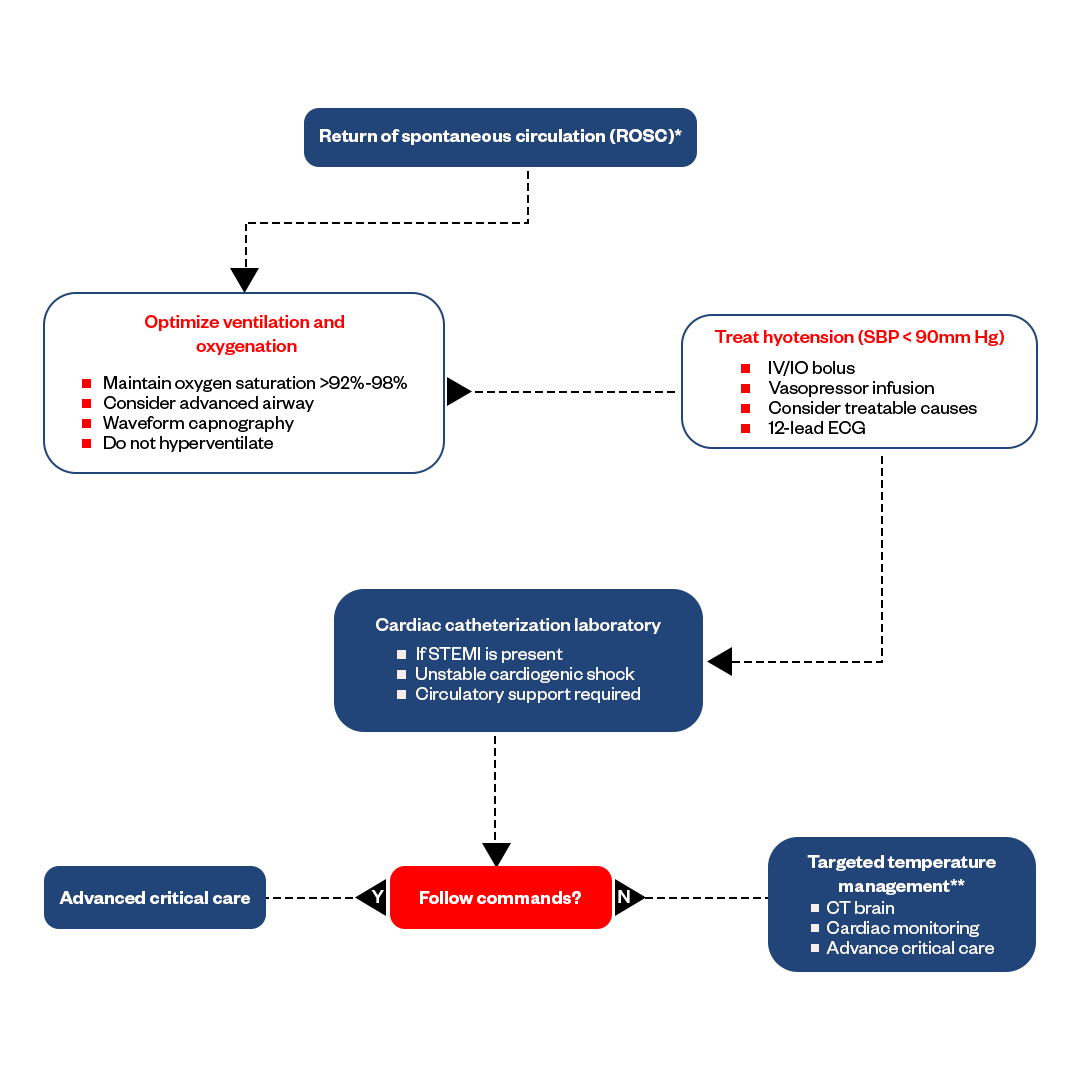
ACLS Algorithm #6: Immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm
Post-cardiac arrest care algorithm is essential for optimal patient recovery. If someone collapses due to ventricular disturbances, immediate action with tools like an AED is crucial. Once resuscitated, the care continues by stabilizing the patient, regulating blood pressure, monitoring cardiac activity, and assessing neurological status. Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) can enhance neurological outcomes, while proper ventilation and hemodynamic stability ensure appropriate oxygenation and systemic perfusion. Modern post-cardiac arrest care, guided by the AHA's recommendations, integrates these aspects to offer patients the best chance of returning to their pre-arrest conditions.
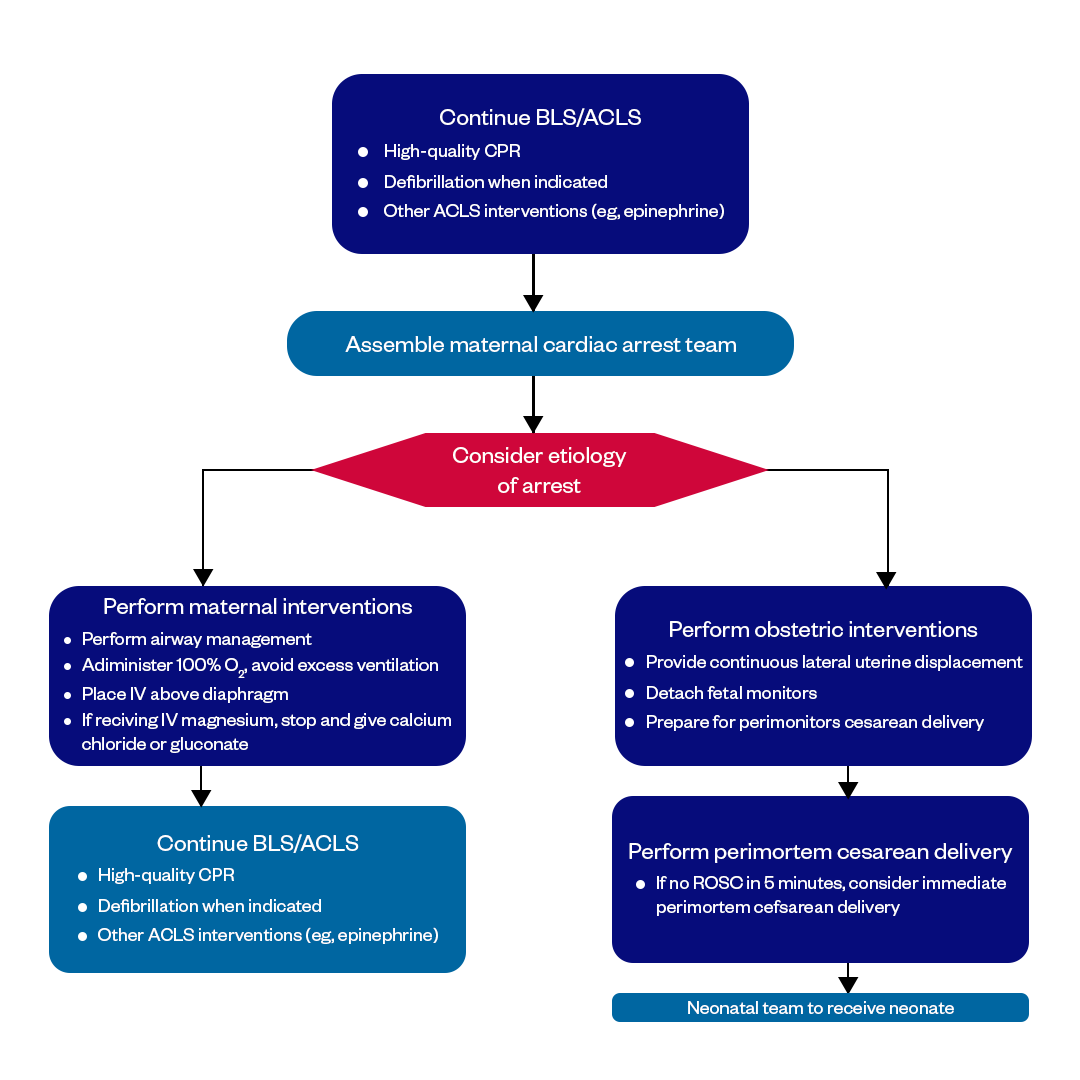
ACLS Algorithm #7: ACLS In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy Algorithm
The cardiac arrest in pregnancy is rare, occurring in only 1 in 30,000 pregnancies but carries a significantly higher mortality rate compared to the general population due to the physiological changes in a woman's body and the need to consider the life of both the mother and fetus. The resuscitation techniques for pregnant women are similar to those for other adults, but there are special considerations due to the dual-patient scenario. Thankfully, the ACLS In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy Algorithm provides a structured, evidence-based approach to managing this critical emergency situation. By following standard ACLS protocols and algorithms, healthcare providers can ensure they are delivering the highest standard of care, improving outcomes in such emergencies where every second counts and informed actions can make all the difference.
Hs and Ts in ACLS Algorithm?
The below are the Hs and Ts in ACLS algorithm also known as reversible causes:
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- Hydrogen ion (acidosis)
- Hyper-/hypokalemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypothermia
- Toxins
- Tamponade(cardiac)
- Tension pneumothorax
- Thrombosis (coronary and pulmonary)
- Trauma
Ready To Register For Your Exam?

100% Online Training Unlimited Exam Retakes 2 Year Certification.

100% Online Training Unlimited Exam Retakes 2 Year Certification.

100% Online Training Unlimited Exam Retakes 2 Year Certification.

100% Online Training Unlimited Exam Retakes 2 Year Certification.
AHA ACLS ALGORITHMS FAQS
Which alteration to the standard ACLS algorithm is appropriate for hypothermia?
During the extrication of a hypothermic cardiac patient to the hospital intermittent CPR is acceptable if continuous CPR is not possible. Withholding ACLS medical until the patient's body temperature reaches 30°C, it is reasonable to give 3 shocks and 3 doses of cardiac arrest medications after then.
What is the highest priority in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithm?
Intermittent CPR can be administered while transporting a hypothermic cardiac patient to the hospital if continuous CPR is not feasible. Delay the administration of ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support) medications until the patient's body temperature reaches 30°C. Additionally, it may be reasonable to consider administering three shocks and three doses of cardiac arrest medications after the patient's body temperature has reached this level.
What are the ABCs of ACLS?
ABC refers to Airway, Breath, and Circulation. It's a common term used by healthcare providers to remember the initial assessment.
What are the 5 lethal rhythms?
Asystole, Ventricle Tachycardia (VT), Ventricle Fibrillation (VF), and Polymorphic Ventricle Tachycardia (Torsade de pointes) are the four lethal rhythms to recognize and review ECG interpretation.
What is the most important algorithm in ACLS?
Well, every algorithm is designed to simplify the recognition and treatment process for a patient having cardiac arrest yet the most important and commonly used algorithm is the cardiac arrest ACLS algorithm.

Owner Jeff Haughy has been providing high-quality care in the EMS industry since 1995 and started his Fire Service career with the Alameda Fire Department in 1991 as a Fire Explorer.