Bradycardia ACLS Algorithm
The ACLS bradycardia algorithm is a part of the Advance Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithm used in emergency medicine to manage patients with bradycardia. Bradycardia is a slow heartbeat condition, typically less than 50 beats per minute.
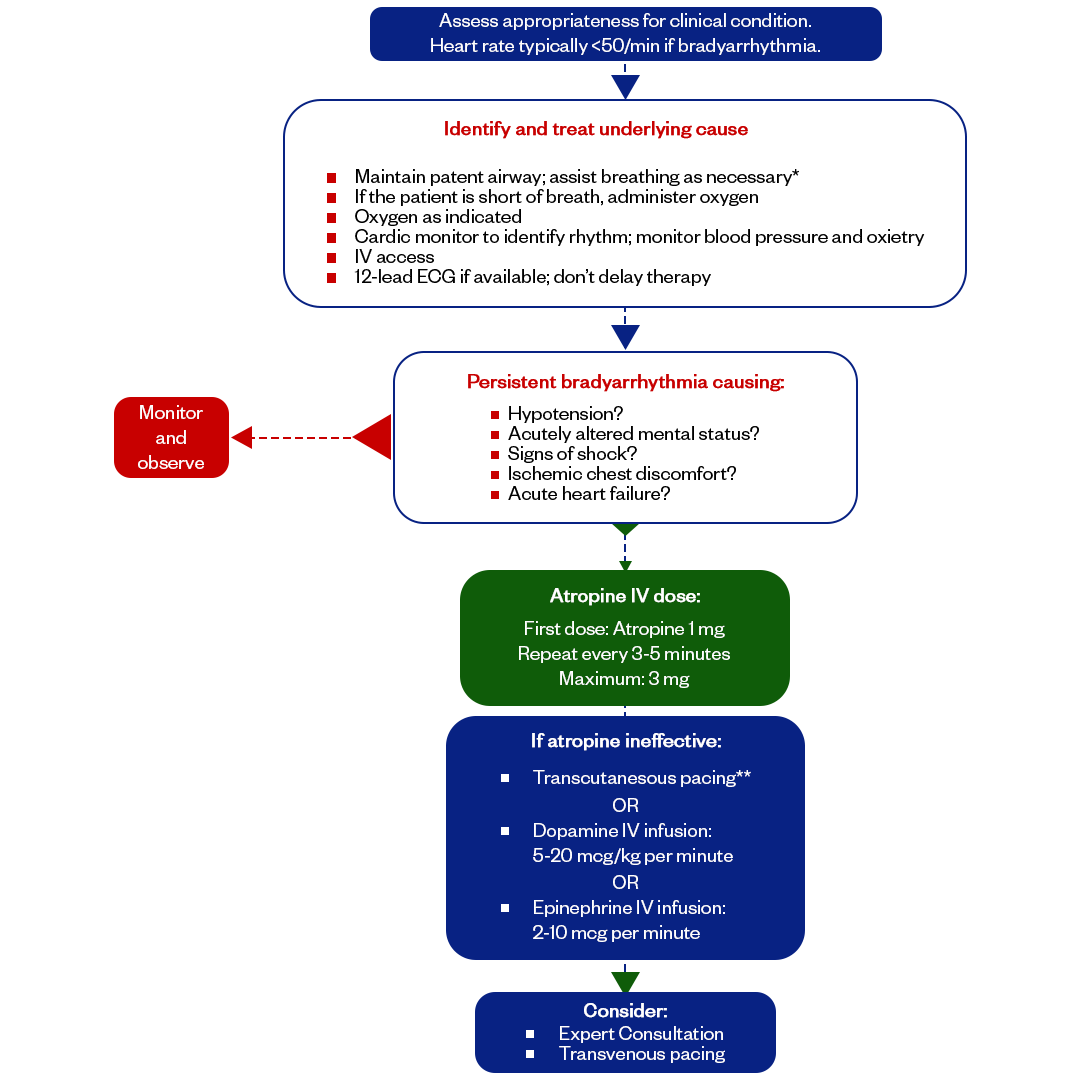
The Bradycardia Algorithm is a structured plan used in Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS).
It involves checking the patient for symptoms and figuring out what might be causing the slow heart rate, making sure their airway is clear, keeping an eye on vital signs such as heart rhythm, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, setting up IV access, and giving appropriate treatments like atropine, transcutaneous pacing, or dopamine/epinephrine if needed.
Overall, it's a step-by-step approach healthcare providers use to handle slow heart rates systematically.
Treatment For The Bradycardia (Algorithmic Approach)
The treatment of bradycardia depends on the clinical condition, symptoms, and the underlying cause of the slow heartbeat of a patient. The treatment is based on controlling the symptoms and identifying the cause using the Hs and Ts of the bradycardia ACLS algorithmic approach. We will later learn about the Hs and Ts, but first, let's look at the surface of bradycardia's treatment.
- Assess the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs) and provide appropriate interventions.
- Monitor the patient's vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Identify the Cause:
- Determine the underlying cause of bradycardia, including hypoxia, hypovolemia, acidosis, toxins, cardiac issues (e.g., heart blocks), or other factors.
- Symptomatic vs. Asymptomatic Bradycardia:
- Assess the patient's symptoms. Bradycardia with hemodynamic instability or symptoms like chest pain, altered mental status, hypotension, or signs of shock requires more immediate intervention than asymptomatic bradycardia.
- Atropine:
- If the patient has symptomatic bradycardia with poor perfusion, consider atropine or transcutaneous pacing.
- The typical initial dose for adults is 0.5 mg IV, which can be repeated every 3-5 minutes, up to 3 mg.
- Atropine is primarily used for bradycardia resulting from vagal stimulation or certain medication overdoses.
- Dopamine or Epinephrine:
- Epinephrine and dopamine are second-line drugs for symptomatic bradycardia. If atropine is ineffective or not indicated, consider using a medication like dopamine or epinephrine to increase heart rate and improve cardiac output.
- Dopamine can be infused at 2-20 micrograms/kg/minute.
- Epinephrine can be administered at 2-10 micrograms/minute doses.
- Temporary Cardiac Pacing:
- In cases of severe bradycardia, unresponsive to medications, or if the patient remains unstable, temporary transcutaneous pacing may be necessary.
- Consult a Cardiologist or Specialist:
- If the bradycardia is related to underlying cardiac conduction disorders (e.g., heart blocks), consult a cardiologist or electrophysiologist for further evaluation and potential permanent pacemaker placement.
Hs and Ts of Bradycardia ACLS Algorithm
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- Hydrogen Ion Excess (Acidosis)
- Hypothermia
- Toxins
- Tamponade
- Tension Pneumothorax
- Thrombosis (Pulmonary Embolism)
- Thrombosis (myocardial infarction)
- Trauma
Fast and Convenient
Take ACLS Classes
*Nationally Accepted
ACLS
CERTIFICATION
AHA ACLS course
State-of-the-Art Facilities
Unlimited Exam Retakes
$260
ACLS
ONLINE CERTIFICATION
AHA ACLS Online Course
100% online training
Unlimited Exam Retakes
$280
Bradycardia Algorithm FAQs
What is the Bradycardia Algorithm?
Bradycardia is a situation where your heart beats slower than the normal rate <50 beats per minute with the presence of symptoms. The Bradycardia algorithm identifies the symptoms and causes to deliver treatment efficiently.
What is the most common cause of bradycardia ACLS?
The most common cause of bradycardia in ACLS scenarios is often related to underlying cardiac conduction abnormalities. Abnormalities such as atrioventricular (AV) blocks or sick sinus syndrome.
What is the first intervention for bradycardia?
The initial intervention for bradycardia involves ensuring airway and breathing support, continuous patient monitoring, oxygen supply, blood pressure and oxygen saturation assessment, and establishing intravenous (IV) access. Additionally, obtaining an ECG is crucial for better rhythm visualization and monitoring.
How do you stabilize bradycardia?
Bradycardia can be controlled with medications like Atropine, Dopamine, or Epinephrine and a temporary heart pacing machine.
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
Symptoms of bradycardia are:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Cognitive impairment
- Palpitations
- Weakness
How is Bradycardia Treated in ACLS?
The go-to medication for managing symptomatic bradycardia, according to the ACLS guidelines, is atropine. Doctors typically administer it at a dose of 1 mg through an IV push, and this can be repeated every 3-5 minutes if needed, up to a maximum total of 3 mg. If atropine doesn't work effectively in treating the symptomatic bradycardia, healthcare providers might consider using dopamine as the next option.
Is CPR Given for Bradycardia?
During bradycardia, chest compressions improve blood flow to vital organs, especially the heart and brain. In adults and children receiving CPR, chest compressions are only given when there's no pulse or when organ perfusion is inadequate.

Owner Jeff Haughy has been providing high-quality care in the EMS industry since 1995 and started his Fire Service career with the Alameda Fire Department in 1991 as a Fire Explorer.